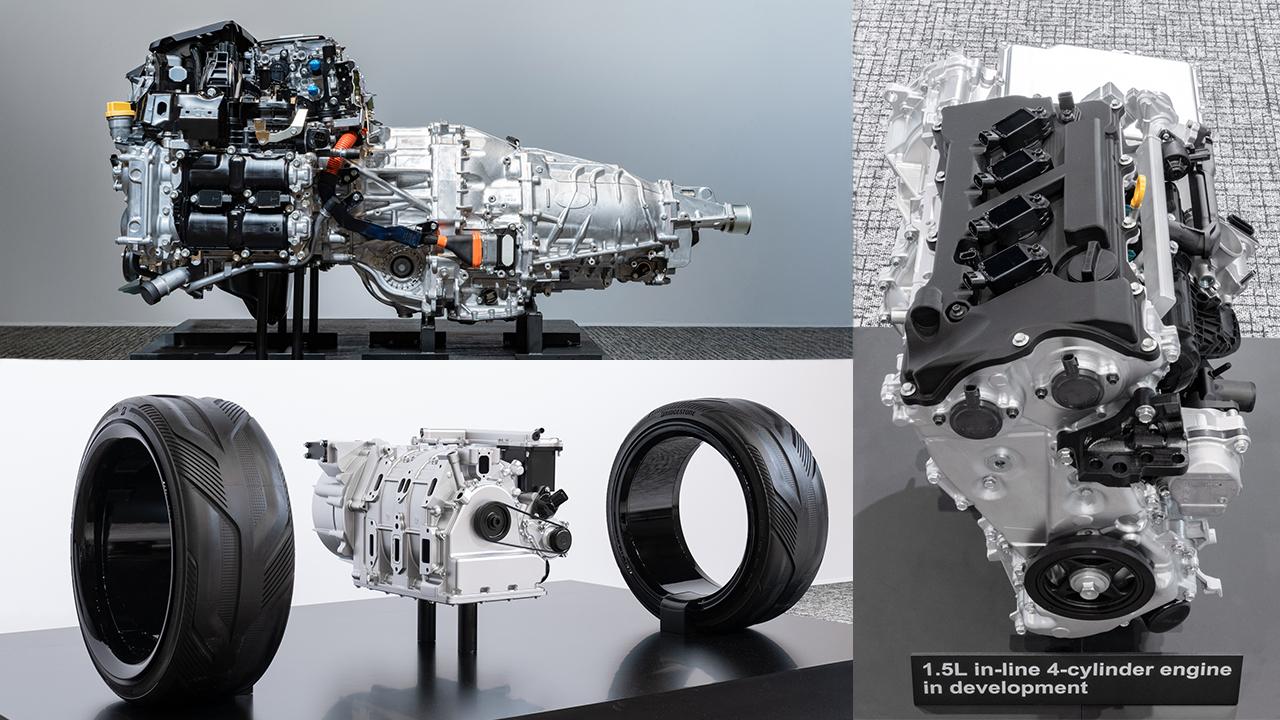
Subaru, Mazda, and Toyota's technology chiefs provided updates on their next-generation engine development. We take an in-depth look at these new technologies, which build on each company's unique offerings.
Reference: Differences between in-line, V-type, horizontally-opposed, and rotary engines
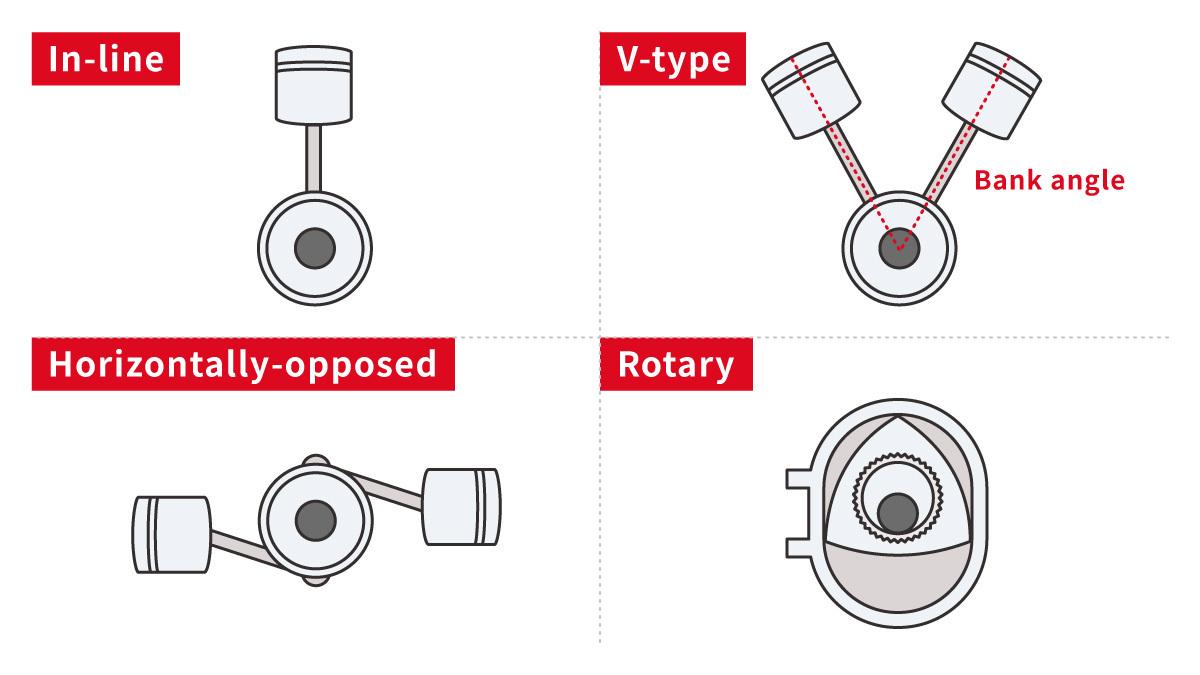
Engines are generally named according to how their cylinders are arranged, with “in-line” indicating a straight row, and “V-type” being a V-shaped configuration alternating left and right.
In a “horizontally opposed” engine, the cylinders are arranged flat, facing each other. The rotary engine stands apart, powered by the revolutions of a triangular rotor.
Horizontally-opposed engines have a low profile and center of gravity. They are also said to have less vibration, since the pistons are positioned on either side of the crankshaft such that their movements balance each other out.
Rotary engines have a simple structure that makes them compact and lightweight yet powerful. In 2023, they were brought back into production after an 11-year hiatus and are now being used as generators rather than to drive vehicles.

